
Overview
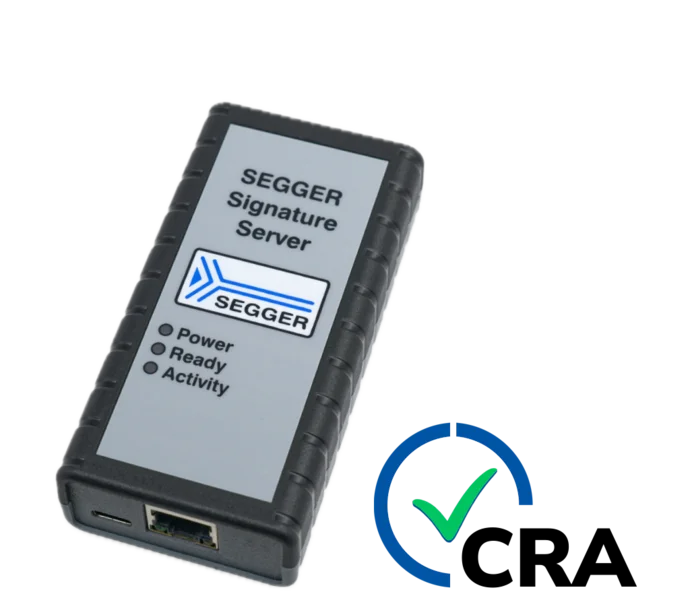

emBoot-Secure is SEGGER’s Cyber Resilience Act-compliant solution for secure and verifiable firmware updates on embedded devices. This end-to-end approach protects embedded devices against unauthorized firmware modifications, intellectual property theft, and device cloning. It ensures that only authentic, manufacturer-approved firmware is installed, using a public-key cryptographic architecture that keeps the private signing key protected at all times.
In the context of the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), secure updateability is a core requirement for modern embedded systems. emBoot-Secure provides a robust foundation for meeting these regulatory demands by protecting devices throughout their entire lifecycle, from production to long-term operation in the field.
Key features

Secure firmware authenticity through digital signatures
All firmware updates are digitally signed using modern cryptographic algorithms. Devices verify the signature before installation, ensuring firmware integrity and reliably detecting any manipulation or unauthorized modification.

Protected update packages with compression and encryption
Firmware update packages are compressed to reduce transfer size and storage requirements. Encryption protects firmware contents during distribution, preventing inspection or reverse engineering while updates are delivered through customer-defined channels.
Seamless integration into production workflows
emBoot-Secure integrates smoothly into existing build and release processes. The Signature Server is added as a dedicated hardware-based signing component that securely holds the private key and performs all signing operations, without disrupting established development or production workflows.
Use cases

Secure firmware updates for consumer devices
emBoot-Secure uses cryptographically secure algorithms instead of simple checksums to detect manipulated firmware. The bootloader verifies firmware integrity before execution and will not start modified or unauthorized firmware. Optionally, a recovery firmware can be installed automatically if manipulation is detected, depending on the customer configuration.
Firmware updates themselves are not fetched by the bootloader. Update delivery is handled by the application software. Once a valid update package is provided to the bootloader, it is securely installed during the next restart.

Secure firmware updates in industrial environments
emBoot-Secure enables reliable firmware updates on devices with limited or no internet connectivity. This is particularly valuable in industrial systems with closed networks, long operating lifetimes, or strict security policies.
Firmware updates can be distributed using customer-defined methods that require physical access, such as USB sticks or SD cards. emBoot-Secure ensures that only authenticated firmware is installed, supporting secure and controlled update processes while maintaining the reliability of industrial equipment.
How emBoot-Secure works
emBoot-Secure follows a complete, end-to-end workflow for secure firmware updates. The process includes cryptographic signing, compression, optional encryption, and reliable installation on the device, integrating smoothly into development, production, and field-update environments.
Key generation
A public–private key pair is created using either the SEGGER Signature Server or SEGGER KeyGen as part of the initial setup.

SEGGER Signature Server (recommended)
The private key is generated and stored securely on the Signature Server. It never leaves this controlled environment, ensuring maximum protection and simplifying compliance with modern security requirements.

SEGGER KeyGen
The key pair is generated on a local PC, giving full local control. The generated private key can later be imported into a SEGGER Signature Server to benefit from its advanced security features. A secure backup of the key can be stored in a safe, for example in a bank.
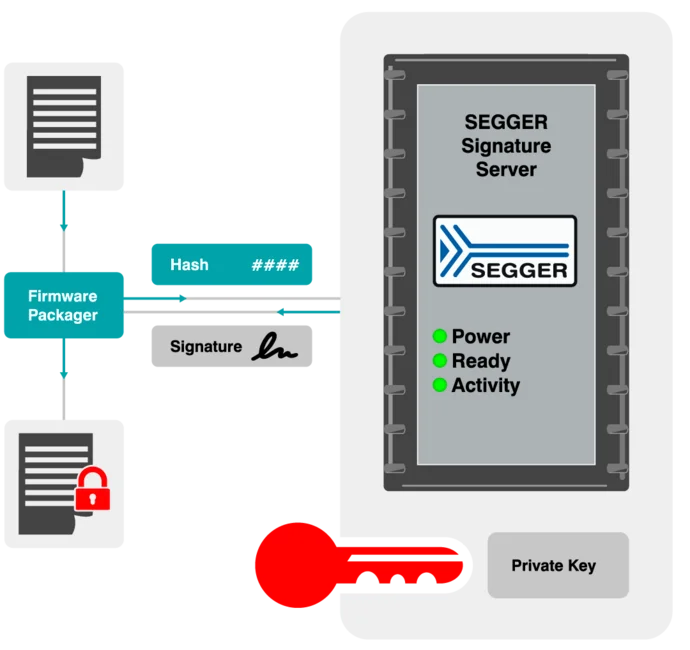
Signing and creating the update package (Firmware Packager)
The Firmware Packager prepares the firmware update package in a single, controlled step. It computes a cryptographic hash of the firmware and sends it to the SEGGER Signature Server. The server generates the digital signature using the securely stored private key and returns it to the Firmware Packager.
The Firmware Packager then creates the final update package, optionally compressing and encrypting the firmware. The result is a compact and authenticated update file that is ready for distribution. Throughout the process, the private key remains protected on the Signature Server.
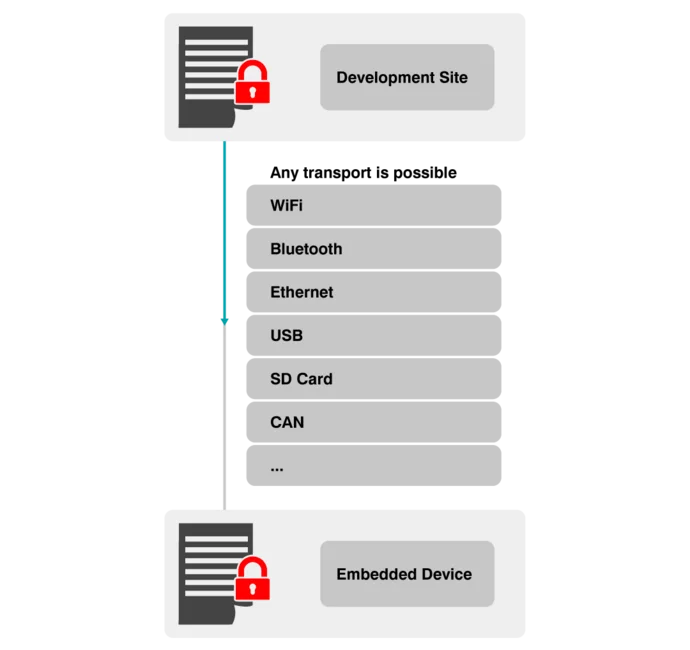
Firmware transfer
The update package is delivered to the embedded device using any customer-supported transport channel, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, USB, SD card, or CAN. The application on the device receives the update and stores it in non-volatile memory until it is processed by the bootloader during a restart.
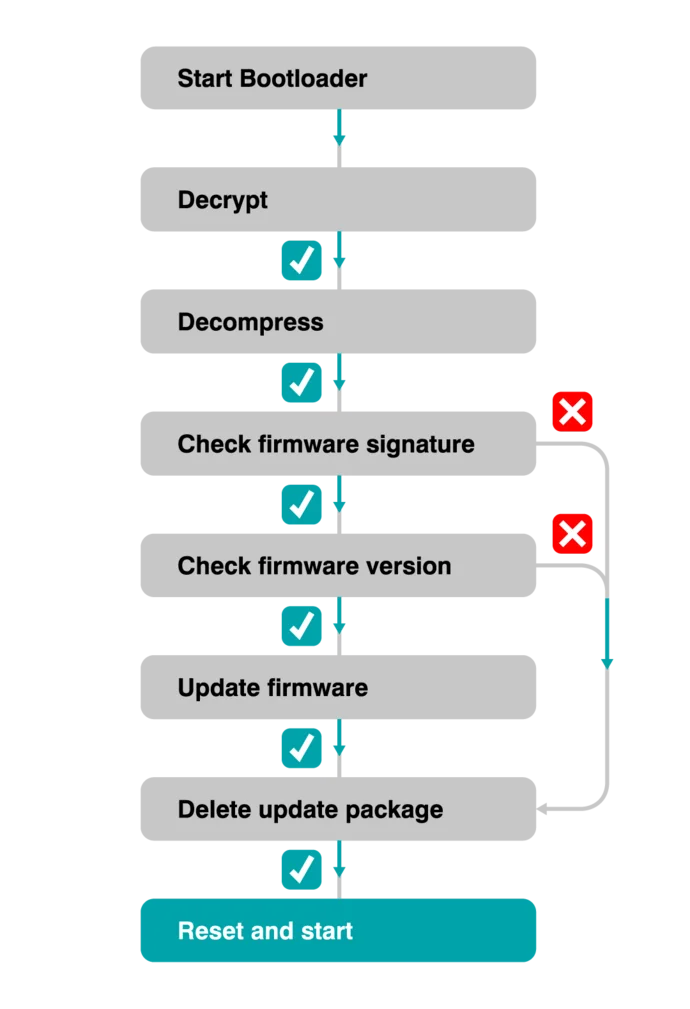
Firmware update
The emBoot-Secure bootloader manages the entire update process on the device. Its behavior depends on whether an update package is present.
When an update package is available:
When an update package is available, the emBoot-Secure bootloader decrypts and decompresses the content if required, checks the firmware signature and version, and installs the update. The update package may be retained so it can be reused if the installed firmware becomes corrupted. If the version is unchanged, the bootloader will not reinstall the firmware.
When no update package is available:
If no update package is present, the bootloader verifies the signature of the existing firmware and, if required, can restore a recovery image before starting the verified firmware.
This mechanism ensures that devices always run authenticated firmware and remain secure and operational at all times.
Supported algorithms
| Signature | RSA up to 8192 bits, ECDSA up to 521 bits (secp521r1) |
| Hash | SHA 1/256/384/512 |
| Encryption | AES-128 .. 256 |
| Compression | SMASH-2, LZMA |

Licensing
The software is available under various embedded software license models and can be delivered as source code. All commercial licenses are based on a one-time payment, are royalty-free, and include six months of updates and support from SEGGER’s Embedded Experts.
There are no subscription fees, ensuring predictable and fixed costs over the entire product lifetime.
For non-commercial use, evaluation, and educational purposes, the software is provided under SEGGER’s Friendly License.
FAQ
Can the bootloader itself be updated?
Yes, the bootloader can be updated in the same way as an application.
Can the SEGGER Signature Server contain or generate an unlimited number of keys?
The Signature Server can store and manage up to 100 keys.
Is the Signature Server optional when using SEGGER KeyGen?
Yes. The Signature Server is the recommended option. Alternatively, SEGGER KeyGen can be used without the Signature Server.
Are other packages (e.g. emSecure RSA/ECDSA) part of the new emBoot-Secure?
The required cryptographic algorithms (RSA and ECDSA) are included as part of emBoot-Secure. The full emSecure source code is not included.
Which ECDSA curves are supported by emBoot-Secure?
emBoot-Secure supports the following curves of the ECC Brainpool working group (RFC5639) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST):
- brainpoolP256r1: 256 bits
- brainpoolP320r1: 320 bits
- brainpoolP384r1: 384 bits
- brainpoolP512r1: 512 bits
- NIST P-256 (secp256r1): 256 bits
- NIST P-384 (secp384r1): 384 bits
- NIST P-521 (secp521r1): 521 bits
These curves cover the recommendations of various regulatory bodies, such as the German Federal Office for Information Security and NIST.
Get in touch with us
Have questions or need assistance? Our Embedded Experts are here to help!
Reach out to us for:
- Licensing quotes
- Technical inquiries
- Project support