emUSB-C PD
Software to manage USB-C power delivery in embedded applications
emUSB-C PD is a complete power delivery protocol implementation for USB-C as defined by USB-IF, especially designed for use in embedded devices.
Overview

emUSB-C PD turns the cable into a smart connection, enabling the detection of the type of device connected, power supply capabilities, USB Host/Device software, and more. With SEGGER's emUSB-C PD library, embedded applications can easily handle a USB-C port on any embedded device with a USB PD controller.
emUSB-C PD can detect whether a connected device is a power source or sink, and even identify USB data roles (host/device). For devices that use USB-C purely as a power source or for battery charging, it supports features such as dead battery signaling, ensuring reliable power management even under challenging conditions.
The library is highly efficient, with ISO/ANSI C source code and a very easy API for straightforward integration into embedded applications. Developers can also configure it for minimal memory footprint, making it ideal for resource-constrained systems. Additionally, emUSB-C PD supports the use of chargers with variable supply voltage, enhancing flexibility for powering devices.
emUSB-C PD can be used in combination with emUSB-Host and/or emUSB-Device. It can also be used without a USB stack for devices that just use USB-C as a power source or to charge a dedicated battery.
Key features
emUSB-C PD offers a robust set of capabilities that make USB-C integration seamless and efficient for embedded systems. These features are designed to optimize power delivery, device compatibility, and ease of implementation
Role swap
Per default, the USB host is always the power source and a device is always the power sink. Using role swaps, a host can be a power sink and a connected USB device can be the power source.
Device connection detection on USB Type-C connectors
The library detects and identifies devices connected to USB-C ports, ensuring compatibility and optimal functionality.
Dynamic power supply negotiation up to 20V 3A
emUSB-C PD enables embedded applications to negotiate power delivery dynamically, ensuring devices receive the optimal voltage and current for their needs.
Use cases
USB-C has additional lines and can transmit more power than previous USB connections. Even for power-hungry applications, the USB cable can transmit enough power from the source as well. This opens specific use cases, mostly related to different models to provide power, and helps embedded system developers meet the requirement of an EU mandate. According to the new EU Common Charger Directive (Radio Equipment Directive 2014/53/EU), all electronic equipment using wired charging technology is required to be powered via USB-C cable.

Avoiding sudden power loss
When a device regularly powered by battery is connected to another device, it could switch off its own power pack and draw the power from the connected device to reduce the drain on its batteries. Or once its batteries start getting depleted, it can ask the other device to provide power avoiding a sudden loss of connection.

Faster charging with USB-C
With traditional USB, power is limited to 5V and 500mA, with 1.5A as the best case scenario with charger detection. This rarely provides enough power to reliably charge a battery and when it does, it definitely takes a long time. With USB-C, the connection can be used to transmit higher voltages and higher currents. To achieve this, the USB-C PD protocol is used to query the capabilities of the cable and to request power from the sourcing device.
How emUSB-C PD works
emUSB-C PD is a software library for embedded applications that fully supports the power delivery protocol implementation of USB-C. It consists of two layers: The device-independent emUSB-C PD protocol stack and a driver to handle the specific target hardware. Drivers are available for several different target hardware controllers.
Both layers are divided into two functional modules: The base module that provides the API for the application and handles the static sensing of the CC pins, and the PD module that is responsible for the power delivery packet communication. The emUSB-C PD API can also be used in connection with a legacy OTG driver to implement OTG functionality on a device without a USB-C connector.

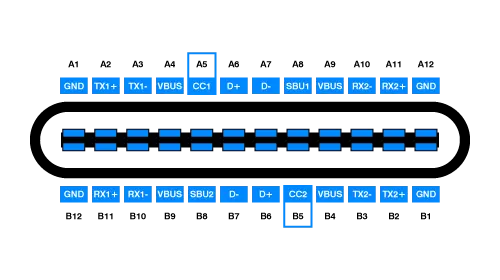
Pinout functions
Typical resource usage
| Function | Code | RAM |
|---|---|---|
| USB-C OTG (on the go) | 1400 bytes | 220 bytes |
| USB-C PD (power delivery) | 5100 bytes | 450 bytes |
| USB-C OTG (sink only) | 1000 bytes | 220 bytes |
| USB-C PD (sink only) | 3800 bytes | 450 bytes |
| USB-C OTG (source only) | 1000 bytes | 220 bytes |
| USB-C PD (source only) | 3300 bytes | 450 bytes |

Licensing
The software is available under various embedded software license models and can be delivered as source code. All commercial licenses are based on a one-time payment, are royalty-free, and include six months of updates and support from SEGGER’s Embedded Experts.
There are no subscription fees, ensuring predictable and fixed costs over the entire product lifetime.
For non-commercial use, evaluation, and educational purposes, the software is provided under SEGGER’s Friendly License.
Get in touch with us
Have questions or need assistance? Our Embedded Experts are here to help!
Reach out to us for:
- Licensing quotes
- Technical inquiries
- Project support